Linux Commands For Developers
-
1. HARDWARE INFORMATION
#Display messages in kernel ring buffer dmesg #Display CPU information. cat /proc/cpuinfo #Display memory information. cat /proc/meminfo #Display free and used memory ( -h for human readable, -m for MB, -g for GB.). free -h #Display PCI devices. lspci -tv #Display USB devices. lsusb -tv #Display DMI/SMBIOS (hardware info) from the BIOS. dmidecode #Show info about disk sda. hdparm -i /dev/sda #Perform a read speed test on disk sda. hdparm -tT /dev/sda #Test for unreadable blocks on disk sda. badblocks -s /dev/sda2. SYSTEM INFORMATION
#Display Linux system information. uname -a #Display kernel release information. uname -r #Show which version of redhat installed. cat /etc/redhat-release #Show how long the system has been running + load. uptime #Show system host name. hostname #Display the IP addresses of the host. hostname -I #Show system reboot history. last reboot #Show the current date and time. date #Show this month's calendar. cal #Display who is online. w #Who you are logged in as whoami3. USER INFORMATION AND MANAGEMENT
#Display the user and group ids of your current user. id #Display the last users who have logged onto the system. last #Show who is logged into the system. who #how who is logged in and what they are doing. w #Create a group named "test". groupadd test #Create an account named john, with a comment of "John Smith" and create the user's home directory. useradd -c "John Smith" -m john #Delete the john account. userdel john #Add the john account to the sales group. usermod -aG sales john4. FILE AND DIRECTORY COMMANDS
#List all files in a long listing (detailed) format. ls -al #Display the present working directory. pwd #Create a directory. mkdir directory #Remove (delete) file. rm file #Remove the directory and its contents recursively. rm -r directory #Force removal of file without prompting for confirmation. rm -f file #Forcefully remove directory recursively. rm -rf directory #Copy file1 to file2. cp file1 file2 #Copy source_directory recursively to destination. If destination exists, copy source_directory into destination, otherwise create destination with the contents of source_directory. cp -r source_directory destination #Rename or move file1 to file2. If file2 is an existing directory, move file1 into directory file2. mv file1 file2 #Create symbolic link to linkname. ln -s /path/to/file linkname #Create an empty file or update the access and modification times of file. touch file #View the contents of file. cat file #Browse through a text file. less file #Display the first 10 lines of file. head file #Display the last 10 lines of file. tail file #Display the last 10 lines of file and "follow" the file as it grows. tail -f file5. FILE PERMISSIONS
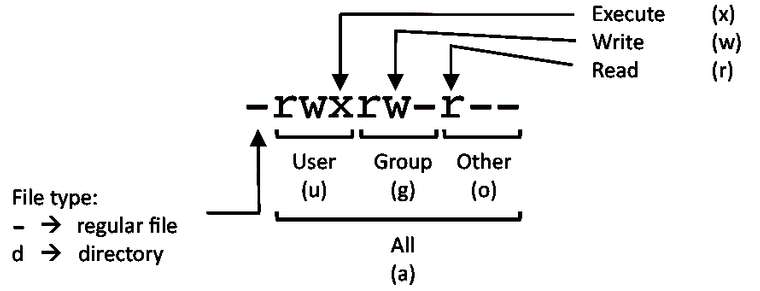
PERMISSION EXAMPLE
U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename6. PROCESS MANAGEMENT
#Display your currently running processes. ps #Display all the currently running processes on the system. ps -ef #Display process information for processname. ps -ef | grep processname #Display and manage the top processes. top #Interactive process viewer (top alternative). htop #Kill process with process ID of pid. kill pid #Kill all processes named processname. killall processname #Start program in the background. program & #Display stopped or background jobs. bg #Brings the most recent background job to foreground. fg #Brings job n to the foreground. fg n7. PERFORMANCE MONITORING AND STATISTICS
#Display and manage the top processes. top #Interactive process viewer (top alternative). htop #Display processor related statistics. mpstat 1 #Display virtual memory statistics. vmstat 1 #Display I/O statistics. iostat 1 #Display the last 100 syslog messages (Use /var/log/syslog for Debian based systems.). tail 100 /var/log/messages #Capture and display all packets on interface eth0. tcpdump -i eth0 #Monitor all traffic on port 80 ( HTTP ). tcpdump -i eth0 'port 80' #List all open files on the system. lsof #List files opened by user. lsof -u user #Display free and used memory ( -h for human readable, -m for MB, -g for GB.). free -h #Execute "df -h", showing periodic updates. watch df -h8. NETWORKING
#Display all network interfaces and ip address. ifconfig -a #Display eth0 address and details. ifconfig eth0 #Query or control network driver and hardware settings. ethtool eth0 #Send ICMP echo request to host. ping host #Display whois information for domain. whois domain #Display DNS information for domain. dig domain #Reverse lookup of IP_ADDRESS. dig -x IP_ADDRESS #Display DNS ip address for domain. host domain #Display the network address of the host name. hostname -i #Display all local ip addresses. hostname -I #Download http://domain.com/file. wget http://domain.com/file #Display listening tcp and udp ports and corresponding programs. netstat -nutlp9. ARCHIVES (TAR FILES)
#Create tar named archive.tar containing directory. tar cf archive.tar directory #Extract the contents from archive.tar. tar xf archive.tar #Create a gzip compressed tar file name archive.tar.gz. tar czf archive.tar.gz directory #Extract a gzip compressed tar file. tar xzf archive.tar.gz #Create a tar file with bzip2 compression. tar cjf archive.tar.bz2 directory #Extract a bzip2 compressed tar file. tar xjf archive.tar.bz210. SEARCH
#Search for pattern in file. grep pattern file #Search recursively for pattern in directory. grep -r pattern directory #Find files and directories by name. locate name #Find files in /home/john that start with "prefix". find /home/john -name 'prefix*' #Find files larger than 100MB in /home. find /home -size +100M11. SSH LOGINS
#Connect to host as your local username. ssh host #Connect to host as user. ssh user@host #Connect to host using port. ssh -p port user@host12. FILE TRANSFERS
#Secure copy file.txt to the /tmp folder on server. scp file.txt server:/tmp #Copy *.html files from server to the local /tmp folder. scp server:/var/www/*.html /tmp #Copy all files and directories recursively from server to the current system's /tmp folder. scp -r server:/var/www /tmp #Synchronize /home to /backups/home. rsync -a /home /backups/ #Synchronize files/directories between the local and remote system with compression enabled. rsync -avz /home server:/backups/13. DISK USAGE
#Show free and used space on mounted filesystems. df -h #Show free and used inodes on mounted filesystems. df -i #Display disks partitions sizes and types. fdisk -l #Display disk usage for all files and directories in human readable format. du -ah #Display total disk usage off the current directory. du -sh14. DIRECTORY NAVIGATION
#To go up one level of the directory tree. (Change into the parent directory.). cd .. #Go to the $HOME directory. cd #Change to the /etc directory. cd /etc -
Installing packages commands posting soon.
-
Thanks <3
-
@Danuva welcome bro
-
nice post :hearts:
-
Great work. 👍Hope to see more from you.
-
@dinlinux Yah, i'll post everything about linux
-
thanx <3