Most Important Terminal Commands For Developers
-
Most Important Terminal Commands For Developers
The terminal is one of the most important tool for software developers in 2019. Mastering it can have a very positive effect on your workflow, as many everyday tasks get reduced to writing a simple command and hitting Enter. In this article i have prepared for you a collection of Unix commands that will help you get the most out of your terminal. Some of them are built in, others are free tools that are time-tested and can be installed in less than a minute.
Git
Git is by far the most popular version control system right now. It is one of the defining tools of modern web dev and we just couldn't leave it out of our list.
There are plenty of third-party apps and tools available but most people prefer to access git natively though the terminal. The git CLI is really powerful and can handle even the most tangled project history.
If you want to learn more about git, i recommend checking out this
SSH
With the ssh command users can quickly connect to a remote host and log into its Unix shell. This makes it possible to conveniently issue commands on the server directly from your local machine's terminal.
To establish a connection you simply need to specify the correct ip address or url. The first time you connect to a new server there will be some form of authentication.
ssh username@remote_hostIf you want to quickly execute a command on the server without logging in, you can simply add a command after the url. The command will run on the server and the result from it will be returned.
ssh username@remote_host ls /var/www some-website.com some-other-website.comThere is a lot you can do with SSH like creating proxies and tunnels, securing your connection with private keys, transferring files and more. You can read more in this guide.
Tree
Tree is a tiny command line utility that shows you a visual representation of the files in a directory. It works recursively, going over each level of nesting and drawing a formated tree of all the contents. This way you can quickly glance over and find the files you are looking for.
tree . ├── css │ ├── bootstrap.css │ ├── bootstrap.min.css ├── fonts │ ├── glyphicons-halflings-regular.eot │ ├── glyphicons-halflings-regular.svg │ ├── glyphicons-halflings-regular.ttf │ ├── glyphicons-halflings-regular.woff │ └── glyphicons-halflings-regular.woff2 └── js ├── bootstrap.js └── bootstrap.min.jsThere is also the option to filter the results using a simple regEx-like pattern:
tree -P '*.min.*' . ├── css │ ├── bootstrap.min.css ├── fonts └── js └── bootstrap.min.jsDisk usage - du
The du command generates reports on the space usage of files and directories. It is very easy to use and can work recursively, going through each subdirectory and returning the individual size of every file.
A common use case for du is when one of your drives is running out of space and you don't know why. Using this command you can quickly see how much storage each folder is taking, thus finding the biggest memory hoarder.
# Running this will show the space usage of each folder in the current directory. # The -h option makes the report easier to read. # -s prevents recursiveness and shows the total size of a folder. # The star wildcard (*) will run du on each file/folder in current directory. du -sh * 1.2G Desktop 4.0K Documents 40G Downloads 4.0K Music 4.9M Pictures 844K Public 4.0K Templates 6.9M VideosThere is also a similar command called df (Disk Free) which returns various information about the available disk space (the opposite of du).
Tar
Tar is the default Unix tool for working with file archives. It allows you to quickly bundle multiple files into one package, making it easier to store and move them later on.
tar -cf archive.tar file1 file2 file3Using the -x option it can also extract existing .tar archives.
tar -xf archive.tarNote that most other formats such as .zip and .rar cannot be opened by tar and require other command utilities such as unzip.
Many modern Unix systems run an expanded version of tar (GNU tar) that can also perform file size compression:
# Create compressed gzip archive. tar -czf file.tar.gz inputfile1 inputfile2 # Extract .gz archive. tar -xzf file.tar.gzIf your OS doesn't have that version of tar, you can use gzip, zcat or compress to reduce the size of file archives.
md5sum
Unix has several built in hashing commands including md5sum, sha1sum and others. These command line tools have various applications in programming, but most importantly they can be used for checking the integrity of files.
For example, if you have downloaded an .iso file from an untrusted source, there is some chance that the file contains harmful scripts. To make sure the .iso is safe, you can generate an md5 or other hash from it.
md5sum ubuntu-16.04.3-desktop-amd64.iso 0d9fe8e1ea408a5895cbbe3431989295 ubuntu-16.04.3-desktop-amd64.isoYou can then compare the generated string to the one provided from the original author (e.g. UbuntuHashes).
Htop
Htop is a more powerful alternative to the built-in top task manager. It provides an advanced interface with many options for monitoring and controlling system processes.
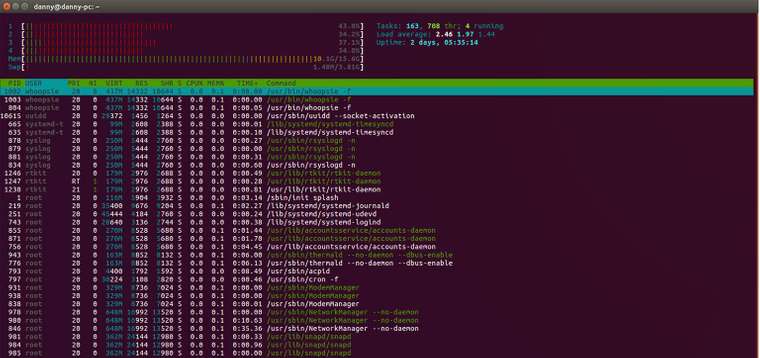
Although it runs in the terminal, htop has very good support for mouse controls. This makes it much easier to navigate the menus, select processes, and organize the tasks thought sorting and filtering.
Ln
Links in Unix are similar to shortcuts in Windows, allowing you to get quick access to certain files. Links are created via the ln command and can be two types: hard or symbolic. Each kind has different properties and is used for different things (read more).
Here is an example of one of the many ways you can use links. Let's say we have a directory on our desktop called Scripts. It contains neatly organized bash scripts that we commonly use. Each time we want to call one of our scripts we would have to do this:
~/Desktop/Scripts/git-scripts/git-cleanupObviously, this is isn't very convinient as we have to write the absolute path every time. Instead we can create a symlink from our Scripts folder to /usr/local/bin, which will make the scripts executable from all directories.
sudo ln -s ~/Desktop/Scripts/git-scripts/git-cleanup /usr/local/bin/With the created symlink we can now call our script by simply writing its name in any opened terminal.
git-cleanupCurl
Curl is a command line tool for making requests over HTTP(s), FTP and dozens of other protocols you may have not heard about. It can download files, check response headers, and freely access remote data.
In web development curl is often used for testing connections and working with RESTful APIs.
# Fetch the headers of a URL. curl -I http://google.com HTTP/1.1 302 Found Cache-Control: private Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 Referrer-Policy: no-referrer Location: http://www.google.com/?gfe_rd=cr&ei=0fCKWe6HCZTd8AfCoIWYBQ Content-Length: 258 Date: Wed, 09 Aug 2017 11:24:01 GMT # Make a GET request to a remote API. curl http://numbersapi.com/random/trivia 29 is the number of days it takes Saturn to orbit the Sun.Curl commands can get much more complicated than this. There are tons of options for controlling headers, cookies, authentication, and more
-
thanks bro... this will be great for every developer.
-
very useful
-
Awesome post😍❤️